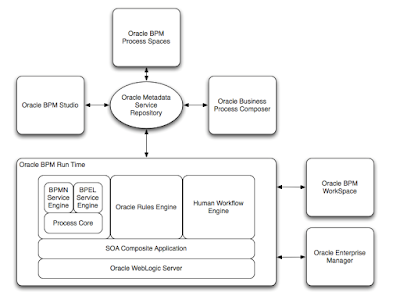
Oracle BPM Runtime
Oracle BPM Runtime or “service
infrastructure” provides the internal message transport infrastructure for
connecting components and enabling data flow. The service infrastructure is
responsible for routing messages along the wire connections between services,
service components, and references.
BPEL Service Engine
For process orchestration of
synchronous and asynchronous BPEL processes.
BPMN Service Engine
For creating and modeling
business processes using Business Process Management Notation and Modeling
(BPMN). The BPEL, BPMN and Process Core (provided shared services for both BPMN
and BPEL engines) are commonly called as BPM engine. According to Oracle documentation, BPMN Service Engine
is actually an extension of the existing BPEL Service Engine and as such it
leverages the core infrastructure of the BPEL. The BPMN Service Engine
leverages JPA/EclipseLink to store/recover the state of a process instance in the
SOA Infrastructure dehydration store maintained by a database and to persist
audit records that are created in the course of running a process. MDS APIs are
used to retrieve metadata Information about the BPMN Process Model and other
BPM project artifacts like the Business Catalog.
Business
Rules Engine
For making a
decision or for processing based on business rules.
Human
Workflow Engine
For modeling a
human task (for example, manual order approval) that describes the tasks for
users or groups to perform as part of an end-to-end business process flow.
This engine is
also used extensively in this tutorial. The details of its services are shown
below.
We can see
that the Human Task Workflow Engine are a major set of SOA components to manage
a wide range of human related services, including routing, roles and
permission, security, timers, interaction with user interface, and
notification.
User Interface and Data Control
Another
important aspect of BPM application is the interaction with users which is
implemented by Oracle ADF. Oracle ADF runs on top of Java Server Faces (JSF)
which abstracts HTML and Java Servlet technologies with web components.
The prominent contribution of Oracle ADF is the ADF Model layer which includes Data Control and Bindings as shown above. Other mechanism is primarily based on JSF infrastructure. The main idea of data control and data bindings is to simplify the process of binding UI elements with various data source in a declarative manner. Developers don’t need to bother with details of various data sources but only work with a common facilities provided by the Data Controls editor in Oracle JDeveloper. We will work with this facility during the human task implementation.
For BPM technology, Oracle provides a special data control called BPM data control which interacts with both BPMN and Human Workflow Engine. It hides the complexity in dealing with these two engines and ease the development efforts.
However, it is noted that Oracle ADF is a huge and complex technology stack on top of JSF, which requires a relatively steep learning curve.
For BPM technology, Oracle provides a special data control called BPM data control which interacts with both BPMN and Human Workflow Engine. It hides the complexity in dealing with these two engines and ease the development efforts.
However, it is noted that Oracle ADF is a huge and complex technology stack on top of JSF, which requires a relatively steep learning curve.